In this article, you can see my
Bluetooth robot. It used for teaching students how to control Bluetooth module (
HC-05) using
Android application. Bluetooth module is controlled by PIC microcontroller
PIC 16F628A, which control motor driver
L293d which control 2 DC motors.
Chassis is made of plexiglass and at next picture you can see dimension of it.
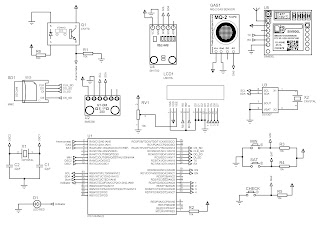
Electrical circuit of Bluetooth robot you can see at next picture.
Android application I made using
MIT App Invertor 2. This app maker it's easy to work then
Android Studio (for someone who don't have knowledge about Android programming in Android studio). Layout of application for Bluetooth robot is at next picture.
As you can see, there is 4 buttons for any direction, and there is a button for connection with Bluetooth (robot) module. Before you want to control your robot, you need to pair your smart phone with HC-05 Bluetooth module (
Settings ->
Connectivity ->
Bluetooth ->
Found new device). Afther that, there will be shown window where you need to write
Pin code for pair module and phone (
1234 or
0000, which depends of Bluetooth module).
After that, you can run application, and pick button
Connect, after that will be open window where you can chose which module you want to connect with (
HC-05). If everithing is OK, button name from
Connect will be change to
Connected. Now your application is ready for control robot.
Lets we back now to PIC microcontroller and how to write code to control robot with received data from Android application.
Compiler I used for writing code for microcontroller is
Proton IDE, it's Basic language. In code you need to set U(S)ART for receiving data from Bluetooth module, test received data and if condition is OK, drive robot. In algorithm you can see steps through code:
First set U(S)ART:
-
Baudrate set to
9600
- Set
RX and
TX register (
RCSTA =
$90 and
TXSTA =
$24 (value of U(S)ART registers)
- Set to
Clear Buffer after every received data
After that, declare variable where microcontroller will put received data. Variable type depend on what you want to send from application. What that mean? If you want to send something like "
Forward", you can't use
integer type (in Proton Basic that is
Byte), you need to declare it like Char (
Word in Proton Basic). In other case, if you want to send "
0" - "
255" you need to use integer type (
Byte).
Now we have to check are we receive some data. If we are, now we check is received data correct, does we have that in condition. If condition is OK, microcontroller go to part of code where we define in which direction we want to drive robot.
For receiving data in Proton Basic you can use
HSerIn where you have to set few parameters,
Timeout (how long microcontroller wait for data (in miliseconds)),
Timeout_label (where code executing go if there is no data) and (modifier)
variable where microcontroller put received data. HSerIn command looks like:
HSerIn Timeout,
Timeout_label, [
Modifier Variable]
For example:
HSerIn 50, Main, [
Dec Variable]
In If command we check is received data equal to any of declared condition:
If Variable
= ???
Then
xxx xxx
xxx xxx
...
xxx xxx
Endif
Checking for condition is in endless loop, thats mean you can drive your robot until you don't empty batteries.
Realization of Bluetooth robot you can see
here.
For
code (
.hex) and application (
.apk) file contact me at my e-mail:
djordjevicpoljak@gmail.com
Enjoy!